Periodontal Disease and Dental Implants
Understanding Periodontal Disease
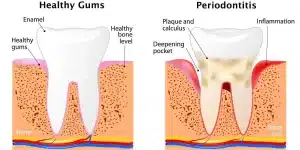
Periodontal disease, commonly referred to as gum disease, is a progressive infection of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in adults. The condition begins with bacterial plaque accumulation around the teeth and, if untreated, advances to destroy the gum tissue and underlying bone. Over time, periodontal disease can severely impact your oral health and quality of life.
What makes periodontal disease particularly concerning is that it often goes unnoticed in its early stages. Many individuals experience mild symptoms such as gum inflammation or bleeding and dismiss them as insignificant. This lack of awareness allows the disease to progress silently, causing irreversible damage. For those who lose teeth due to this condition, dental implants can offer a durable and effective solution.
How Periodontal Disease Affects Oral Health
The damage caused by periodontal disease is not limited to the gums. As the infection advances, it spreads to the bone that supports the teeth, leading to its gradual deterioration. Without sufficient bone support, teeth become loose and may eventually fall out. Furthermore, the bacteria involved in periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream, contributing to systemic health problems such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
Beyond its physical effects, periodontal disease also takes an emotional toll. Tooth loss can lead to a lack of confidence, difficulties with speech, and challenges in eating. Fortunately, dental implants can address these issues by restoring both the function and aesthetics of your smile.
Prevention of Periodontal Disease
Preventing periodontal disease is entirely possible with a commitment to good oral hygiene and regular dental visits. Prevention not only protects your teeth and gums but also ensures a strong foundation for treatments like dental implants, should they become necessary in the future.
Essential Practices for Gum Health
- Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste. Make sure to clean along the gumline, as this is where plaque often accumulates.
- Flossing: Daily flossing is essential to remove debris and plaque from between your teeth and below the gumline, areas your toothbrush cannot reach.
- Mouthwash: Antibacterial mouthwashes can reduce harmful bacteria and freshen your breath, providing an extra layer of protection against gum disease.
- Dietary Choices: A balanced diet rich in vitamins C and D, calcium, and antioxidants strengthens your immune system and supports gum health.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking weakens your immune system and impairs your body’s ability to fight off infections, significantly increasing the risk of gum disease.
- Dental Checkups: Professional cleanings and dental exams are crucial for identifying and addressing early signs of periodontal disease.
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
Identifying the symptoms of periodontal disease early is critical for effective treatment. The condition progresses through stages, with symptoms becoming more severe as the disease advances.
Common Early Symptoms
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath or a metallic taste in the mouth
Advanced Symptoms
- Receding gums that expose more of the tooth
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Painful chewing or sensitivity
- Pus-filled pockets around the gums
If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a dental professional immediately. Early intervention can prevent further complications and may save your teeth from extraction.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
The treatment of periodontal disease depends on the severity of the condition. In its early stages, non-surgical interventions can be highly effective, while advanced cases may require surgical procedures and tooth replacement options such as dental implants.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments focus on eliminating the infection and preventing further progression of the disease. These include:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths the tooth roots to discourage bacterial growth.
- Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics may be used to target and reduce bacterial infection.
Surgical Treatments
Advanced periodontal disease often requires surgical intervention to repair damage and restore oral health. Surgical options include:
- Gum Grafts: Replacing lost gum tissue to protect exposed tooth roots.
- Bone Grafts: Restoring lost bone to provide a stable foundation for dental implants.
- Pocket Reduction Surgery: Reducing the depth of gum pockets to limit bacterial accumulation.
The Role of Dental Implants in Periodontal Disease Recovery
Dental implants are a transformative solution for individuals who have lost teeth due to periodontal disease. Unlike dentures or bridges, implants are anchored directly into the jawbone, mimicking the function of natural tooth roots. This not only provides unparalleled stability but also helps maintain bone density by stimulating natural bone growth.
For patients with a history of periodontal disease, ensuring that the gums and jawbone are healthy before implant placement is critical. In cases of significant bone loss, bone grafting may be required to prepare the jaw for implant surgery. Once the implants are placed, they can restore both the function and appearance of the smile, allowing patients to eat, speak, and live with confidence.
The Connection Between Gum Health and Overall Health
Periodontal disease is not just an oral health issue—it has been linked to systemic health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory infections. Chronic inflammation caused by gum disease can have far-reaching effects on the body, emphasizing the importance of timely treatment.
By addressing gum disease and restoring missing teeth with dental implants, patients can improve their overall health and reduce the risk of developing related conditions. This holistic approach to care highlights the interconnectedness of oral and systemic health.
Benefits of Dental Implants for Gum Disease Patients
For individuals recovering from periodontal disease, dental implants offer numerous benefits, including:
- Longevity: With proper care, dental implants can last a lifetime, making them a cost-effective solution over time.
- Functionality: Implants allow patients to chew and speak naturally, restoring their quality of life.
- Aesthetics: Custom-designed crowns blend seamlessly with natural teeth, creating a beautiful smile.
- Bone Preservation: Implants stimulate bone growth, preventing further bone loss and maintaining facial structure.
Conclusion
Periodontal disease is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss and systemic health issues if left untreated. However, with early detection, effective treatment, and the use of dental implants, patients can regain their oral health and confidence. Dental implants not only restore the function and appearance of your smile but also provide long-term benefits for your overall well-being.
If you are struggling with the effects of periodontal disease, consult with a dental professional to explore your options. Dental implants may be the key to a healthier, happier future.